Nomenclature of Norwegian ships
The Norwegian navy was starving in 1939. It consisted of four Antediluvian coastal battleships (1897 and 1900) of the
Norge and
Haarfarge classes, three ww1-vintage
Draug class destroyers (1908), 26 second-class torpedo boats and three first-class TBs. These were recent
Sleipner class coastal torpedo boats, three more in construction.
Three submersibles class A (1913) and six class B (1922), the minelayer Olaf Tryggvason (1932), Fröya, and two class Glommen (1916), the old sloops Sars and Heimdal (1892 and 1900), and seven light gunboats dating from 1878 to 1886, plus the modern but weak patrol ships Nansen (1930), Nordkapp and Senja (1937) completed this nomenclature in April 1940. Alto in construction were the Aalesund class DDs, Odin class TBs and Otra class minelayers. However hundreds of fishing trawlers were mobilized as patrol ships and several whalers were converted as minelayers.
Coastal Battleships
We will not dig deep into these ships as they are already covered pretty well in the WW1 section.
Norge class (1900)
The British-built, 1900 Eidsvold class were the backbone of the Norwegian Navy until the German invasion of Norway in 1940. They were supposed to be replaced by the more modern and powerful Bjørgvin-class coastal defence ships in 1915, but both were requisitioned by the RN and used as HMS Glatton and Gorgon during WW1.
HNoMS Norge and Eidsvold were sunk during the
first Battle of Narvik. Their heavy armament was more capable than the 270 mm pieces carried by the old gunboats of the 1870-80s converted as minelayers (see below), and comprised for each ship, two 210 mm (8.26 in) guns in single turrets fore and aft, six 15 mm (5.9 in) guns, either side in casemates, eight 76 mm (3 in) guns, four mounted in the battery and the other fore and aft.
In addition they had four 4.7 cm (1.85 in or 3-pdr) QF for self-defence against torpedo boats plus two 450 mm (18 in) submerged torpedo tubes. It seems they had not been modernized. When the invasion broke out, both ships were at Narvik and HNoMS was sank by German destroyer Wilhelm Heidkamp (Z21) and HNoMS Eidsvold by Bernd von Arnim (Z11).
Haarfarge class (1900)
 Models of the two battleships, showing the Eidsvold and Tordenskiold.
Models of the two battleships, showing the Eidsvold and Tordenskiold.These slightly older vessels (HNoMS Tordenskjold and Harald Haarfagre) were considered 'unfit for war' in 1940 but they were active nonethess in April. Very close to the Norge class in terms of general design, they displaced 3,858 long tons (3,920 t) for 93 m long, were built in UK in pre-dreadnought fashion with single turrets and protected by Harvey armor plates, with a belt of 7–4 in (178–102 mm) and turrets 8–5 in (203–127 mm) thick. Armament was about the same as the Norge class. They used Coal-fired vertical triple-expansion steam engines, 3 horizontal boilers, they were capable of 16.9 knots (31.3 km/h; 19.4 mph).
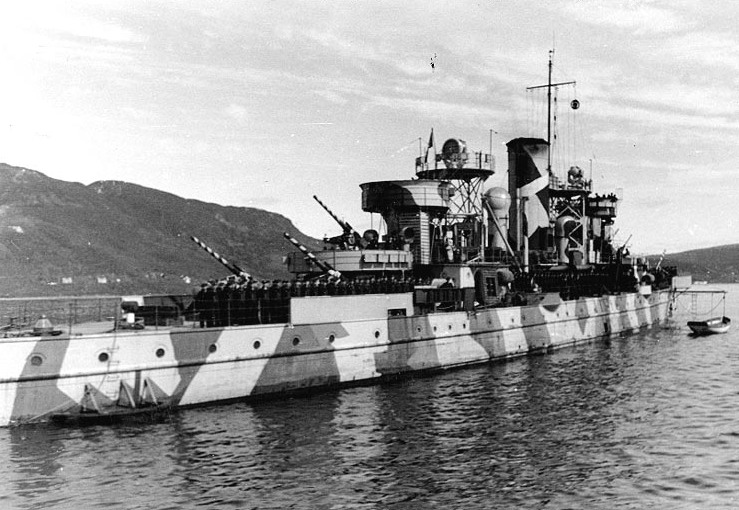 KMS Nymphe as rebuilt and camouflaged, in a Norwegian HarbourGerman Reconstruction
KMS Nymphe as rebuilt and camouflaged, in a Norwegian HarbourGerman ReconstructionAs rebuilt as a FLAK-Schiffe, Tordenskjold became KMS Nymphe, armed with six 10.5 cm AA guns, placed fore and aft of the main superstructure and additional positions for two 40 mm AA guns and fourteen 20 mm AA guns.
 KMS Thetis, Flak-ship, converted from HNoMS Harald Haarfrage (the blueprints).
KMS Thetis, Flak-ship, converted from HNoMS Harald Haarfrage (the blueprints).
Destroyers
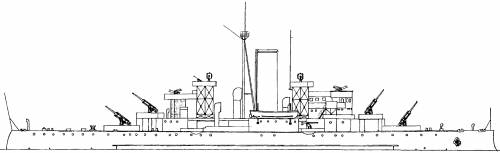
Draug class (1908)
These three locally-built prewar destroyers, Draug (1908), Troll (1909) and Garm (1913), displacing 540 to 578 tons, were built at Horten Yards. They superficially looked like American prewar destroyers with their four funnels, but it's difficult to see a definitive influence there. They were propelled by two VTE engines rated for 8000 hip for the first two, and Garma tried German turbines instead. She was the fastest at 27.4 knots. The two others were capable of 26.5 and 27 knots respectively.
Their boilers were coal-fired, and they carried 105 tons. Their armament was conditioned by their small size, six 76 mm (3 in) guns under masks, one at the front in a superfiring position, one on the roof aft and two amidship, each side of the funnels, as well as the two single trailing tubes. The third 357 mm (18 in) tube was axial, posted at the stern.
Their operation record shown though they were still enlisted, they had been already mothballed before 1939. They were recommissioned but were in poor conditions and needed some care to became fully operational again. They were considered fit only for escort and guard service and were part of the 1st Destroyer division at Bergen in early 1940. However as the German invasion was imminent, moved towards Norwayall three ships were transferred to the 2nd Naval District in south- and mid-western Norway and separated, Draug at Haugesund, Garm at Bergen and Troll at Måløy. Draug duelled with German transports on her way to UK on 9 April 1940.
Garm was later sunk by Stukas at Bjordal, Sognefjord, on 26 April 1940. Troll was abandoned by her crew at Florø and later captured by German forces which used her for specialized roles like an heating barge in the shipyard at Laksevaag. Draug would actively serve as an escort ship with the allies until 1945.
Aalesund class
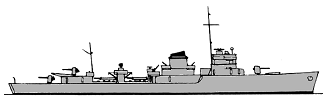 Probable appearance of the Aalesund class according to summary blueprints (Conway's).
Probable appearance of the Aalesund class according to summary blueprints (Conway's).These three ships were in construction in Horten yards when the Germans invanded Norway. Unfotunately they had been started when war became probable, laid down in April 1939. The first was named Aalesund but the second was unnamed. They were substantial ships and would have been very interesting, original ships if built.
As destroyers for 1940 standards they were still small, scale d down to Norway's need but still packed a punch. They were 1220 tons, 100 m long ships, propelled by Turbines to 34 knots, and their armament was to include four 120 mm guns (forward twin mount, two single masked guns at aft in a superfiring pair), two 4 mm Bofors AA located behind the funnel and before the TT banks, two 13 mm AA located fore and aft of the funnel in nacelles, and two twin 533 mm TT banks, which was still weak for DD standards though.
Captured on the stock, both destroyers were to be completed for the kriegsmarine, at first as TA7 and 8 and renamed ZN-4 and 5 ('Zerstörer - Norge'). Fortunately, Norwegian resistance succeeded in sabotaging the construction, resulting in massive delays. German modifications would have included a 1694 tons displacement, single quadruple 533 mm torpedo tubes bank, two 37 mm AA FLAK 38, and six 20 mm AA. Radius was to be 3100 nm for 19 knots. They were never completed, even by the Norwegians after 1945 as their design was already abosolete and needs were covered already by modern British destroyers, and broken up in 1950.
Torpedo Boats
The order is given from the oldest to the most recent.
Odin class TBs (1936)
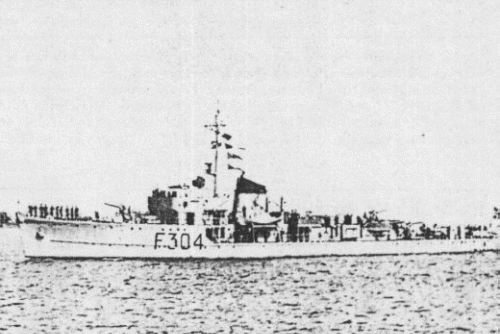
The follows-up of the successful Sleipner class, they were laid down in 1938. Two were built at Horten N Yd (Odin and Balder) and the third, Tor, was to be built at Frederickstad Mek Verstad. Only Odin was in service in April 1940, she has been launched in January 1939 and the two others in October 1939 and September 1939 respectively.
They were improved on certain details but otherwise similar so the sepcs remains the same except they had just two 102 mm guns instead of three. Odin surrended at Kristiansand in 11 April 1940, but Balder and Tor were captured while fitting out. They were completed by the Germans to be used as Leopard and Tiger, armed with a single 102 mm, 2-4 x 40 mm AA, two 8 mm MGs, and the TTs were removed. They were retroceded in 1945 and served until 1959, modernized like the Sleipner class ships as Frigates.
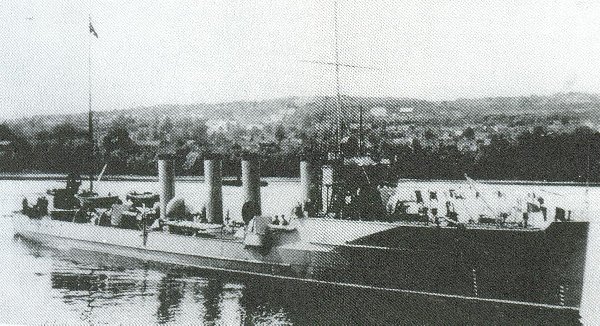
Sleipner class TBs (1936)
 ONI archive recognition plate of the TB-43-46 in German service. Its aspects is significantly different from the original design.
ONI archive recognition plate of the TB-43-46 in German service. Its aspects is significantly different from the original design.
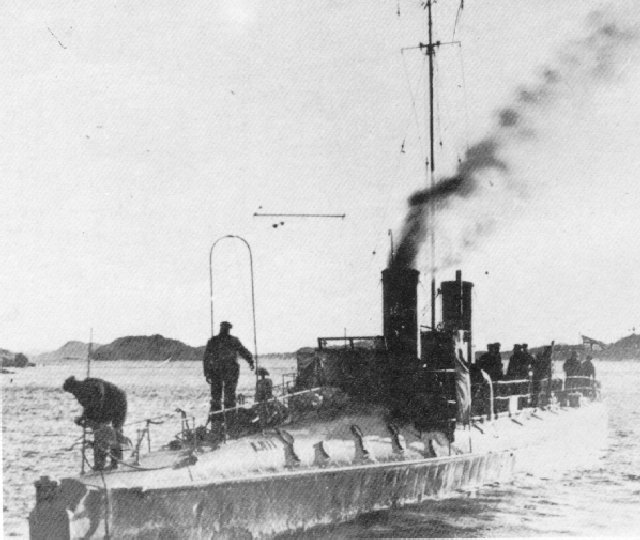
Certainly the most potent and most modern ships of the Norwegian navy, the Sleipner class torpedo boats were ordered in 1933 and laid down in 1934, 35 and 37 as Sleipner, Aeger and Gyller at Horten naval Yard. They were still small even for 1930s TBs at 708 tons fully loaded, but were capable of 30 knots, armed with 21-in torpedoes and capable of minelaying operations. Indeed rails were fitted to their deck, running from the forecastle. In addition they also carrier four ASW deep charge launchers.
Their artillery was not ridiculous either with three 102 mm/40 (4 in) under masks, positioned on the forecastle, and two in superfiring pair aft. The twin torpedo tubes bank was placed behind the single funnel. Between N°2 gun and this bank was located the 40 mm Bofors AA gun. This made these ships quite versatile warships. The design was such a success it was repeated on the next Ordin class (in construction when the war broke out), they served with the Kriegsmarine and back with the Norwegian Navy as frigates right up to the late 1950s.
Sleipner escaped to UK and served with the Free Norwegian Navy until 1945. Aeger was bombed by the Luftwaffe on 9 april 1940 and Gyller surrendered at Kristiansand on 11 April. She served as the German Löwe until 1945 and was retro-ceded to the Norwegians. She served until 1959 and Sleipner until 1956. At that time they had been comprehensively modernized, with modern electronics, three QF automated 76 mm (3 in) AA guns, two Bofors 4 mm and two 20 mm AA guns and fitted for minelaying.

Sleipner class Specifications
Displacement: 597 - 708 tons FL
Size: 72 m - 74.30 m oa L x 7.80 x 2.10 (243 x 25 x 6 ft)
Machinery: 2 shaft De Laval Turbines, 3 Yarrow boilers, 12,500 hp, 30 knots
Radius: 3500 nm at 12 knots
Armament: 3x 102 mm/40, 1x 40 mm AA, 2 MG, 2x 533 mm TTs, 4 DCT, mines.
Snögg class TBs (1919)
These postwar large torpedo boats were the first 1st class high seas TBs of the Royal Norwegian Navy. They displaced 256 tons, for 53x 5.5 x 1.8 m in size (173 x 18 x 5 feets), were powered by two shafts VTE rated for 3500 ihp (2 boilesr), oil-fired, with 33 tons carried. They were capable of 24-15 knots and were armed by two 76 mm (3 in) guns and two twin banks of 457 mm (18 in) torpedo tubes, plus mine tracks were fitted on their decks. They are references also as Trygg class, entering service in 1920-21.
They were perfectly active in WW2. Snögg has been abandoned in April 1940, and was captured, served into the kriegsmarine until 1943 as V5504. She was beached at Bergen until the end of the war. Stegg was one of the rare ship sunk in combat, duelling on 20 april 1940 against the German ship KMS Bremse at Heröysund (Hardangerfjord). A hit exploded one of her torpedoes. Trygg was also sunk in action by Stukas on 22 April at Aandalses but she was recovered and repaired by the Germans and became V5503. She was sunk by the allies at Hjelterfjord in 1944.
Teist class TBs (1907)
These 92/108 tons boats were among the most modern in WW1 and still were serviceable in WW2 as well, active in 1940. They measured 41.1 m by 4.7 m by 2.3/2.4 m draught (134.1 x 15.5 x 7.7 feets.inches). They had one single shaft driven by a VTE fed by two coal-burning boilers rated for 1700 hp, enough to reach 25 knots, carrying 15.4 tons of coal. They were armed by two 47 mm guns or a single 76 mm (3 in) and three 357 mm (18 in) Torpedo Tubes, in the bow and two aft axial ones. Teist was scuttled at Drange, Skarv was captured at Egersund, Kjell in drydock at Kristiansand, and she became the KT-1 and later Grenadier patrol boat.
Ravn class TBs (1903)
Thes five 70 tons coastal TBs (Ravn, Örn, Lom, Jo, and Grib) were blown up by their crews to avoid capture off Lyngör but two others (örn and Lom) were captured under repairs at Horten, renamed Schlange and Eidesche and used as patrol crafts until 1945.
Hval class TBs (1896)
Built in 1895-1902 these nine coastal TBs, VTE with coal-burning boilers, 84 tons, were in part mothballed in the interwar. Hval was striken in 1931, Delfin in 1927, Trods circa 1933, and the remainder boats (Brand, Storm, Skrei, Sael, Sild and Laks) were in semi-active service in 1939. Hval and Delfin were captured and reused by the Germans despite their poor condition, mothballed fro years but not scrapped. Brand was captured at Laksevaag on 11.4.1940 and renamed Tarantel in German service and later NB19 and V5519. She survived and was retroceded in 1945. Sael was attacked and sunk by S-Bootes, Laks captured under repairs but left unrepaired and unused by the German navy.
Hvas class TBs (1898)
These four ships were 64 tons, VTE-powered coal-burning ships launched between 1898 and 1903. They were named Hvas, Kjaek, Falk and Hauk. They were all reactivated when the war broke out and in the process of reconversion as minelayers in April 1940. They were captured in 12-17 April and were used as the patrol boats NO23-26 by the Germans until May 1945.
Varg class TBs (1894)
These very old 45 tons TBs (Hvas, Raket, Glimt, Blink, Djerv, Kvik and Dristig) dating back 1894-98 has been partially reformed during the interwar. The three oldest were scrapped in 1923, but the others were operating as patrol crafts. Blink, Lyn and Kvik were captured in April 1940 and pressed into German service as KT2-4, then renamed Kürassier, Musketier, Dragoner, then NK02-04. They were retro-ceded in May 1945 and BU. Djerv and Dristig were being reconverted as minelayers in April 1940 when scuttled to prevent capture. They were even older boats in the inventory in 1923, The three 36 tons Odd class, all scrapped that year.
Submarines
B1 class submersibles (1923)
This six units built at MV Horten (B1-B6) in 1923-30 had rocky beginnings: These were single-hulled submarines of the Holland type, built in Norway under US design, the first one was laid down in 1915. They were launched in 1922-29 and were outdated when ww2 broke out. As customary for Holland boats they were fast and agile underwater but slow on the surface. Top speed was 14.5 knots and they were armed with a deck gun, 76 mm/28 Bofors, plus four 450 TTs (in the bow, with 6 torpedoes in reserve).
The Submarine B1 fled to UK in July 1940 and stayed there for training until July 1944. B2, B4, B5 and B6 were captured by German troops at Kristiansand, Horten and Florö, or the Sunn-fjord between 9 april and 18 may. The first two were broken up, B5-B6 were eventually repaired, overhauled, and re-commissioned by the Kriegsmarine as UC1 and UC2 in November 1940 and 1941. They used for training. UC1 was broken up and UC2 scuttled in May 1945. B3 was scuttled at Tromsö on the 9 june 1940 to avoid capture.
Specifications
Displacement: 420/545 tons
Dimensions: 51 x 5.33 x 3.5 m
Propulsion: 2 shafts Sulzer diesels/2 electric motors 900/700 hp
Top speed: 14.5/10.5 knots surface/underwater - Radius 2900 nm(9)/150 nm(3)
Armament: 1 x 76mm/28 Bofors, four 450 mm TT tubes (bow, 6)
Crew: 23
Max diving depth: 60 m
A2 class submersibles (1914)
These WW1-era submersibles were all ordered to Germaniawerft, Kiel, Germany just before the war broke out. They were typical of the early generations of German U-boats, laid down in 1911, launched 1912 and completed in 1914. The contract concerned four boats, but when the war broke out, the fourth, A5, has been requisitioned by Germans, commissioned as U0 (later UA). They served for the whole interwar and in 1940 they were outclassed but still cane provide some costal defense. A2 was captured by Germans in Oslo-fjord (Bulerne island) on 9 march 1940, sold for scrap. A3 and A4 were scuttled by their crews on the 15 april 1940 in Tönsberg-fjord.
Specifications
Displacement: 420/545 tons
Dimensions: 46.5 x 4.8 x 2.7 m
Propulsion: 2 shafts Germania diesels/2 electric motors 700/380 hp
Top speed: 14.5/9 knots surface/underwater - Radius 900 nm(10)/76 nm(3)
Armament: Three 450 mm TT tubes (2 bow, 1 stern, 5 reserve)
Crew: 17
Max diving depth: 50 m
Miscellaneous
MTB1 class motor torpedo boats (1939)
These four BPB 60ft MTBs were ordered in UK. They were however all requisitioned by the British Government when the war started, re-commissioned by the Royal Navy as motor gunboats as MGB40-43.
OTRA class minesweepers (1939)

These dedicated minesweepers were built at Nyland, Oslo, built in 1939 and in service the same year. They were fitted with a mechanical minesweeping gear and could carry mines as well. They were captured at Horten by German troops on 9 April 1940, commissioned by the Germans as KMS Togo and Kamerun, returned later to Norway after the war and commissioned again in 1947 as minelayers.
Specifications
Displacement: 320/370 tons
Dimensions: 52.1 x 7 x 1.8-2 m
Propulsion: 2 shafts VTE, 900 hp
Top speed: 13.5 knots - Radius 1400 nm(9 knots)
Armament: 1x 40 mm/56 Bofors, 2x 20 mm/70 Oerlikon, 2x 12.7 mm/90 HMG
Crew: 25
 HNoMS Otra testing at Nyland shipyard
HNoMS Otra testing at Nyland shipyard
Minelayer OLAF TRYGGVASON (1934)

The very capable, large vessel was built at MV Horten, laid down in 1931, launched in 1932 and commissioned in 1934. HNoMS Olav Tryggvason has been fitted with a very original powerplant, comprising two De Laval geared steam turbines fed by 3 boilers and as auxiliaries, tw 8-cyl diesel-generators and two electric motors. She was armed by a single 120 mm/44 Bofors, one 76 mm/51 Bofors AA and 2x 40 mm/56 Bofors, plus two 12.7 mm/90 heavy machine guns, possibly two twin 450 mm TTs and 280 mines.
The naval press was unanymous about this minelayer, one of the most perfect worldwide when introduced into service. Her original machinery included two geared steam turbines (6000hp) and two diesel-generators. The latter fed the equivalent of 1400hp. The long cruise of the ship still allowed to reach if needed 14 knots under diesels, but under turbines this was 21 knots and she even achieved 23kts at trials.
Due to the local bad weather, Olav Tryggvason had a covered mine deck, while the mines dropped through three stern gangway ports. Sources are conflicting about her twin TT bank, a sources diverge between one twin 450mm TT (centerline) or 2 twin 450mm TT (one each side), at least as designed. Indeed under commissioned by the German Navy, she had none.Olaf Tryggvason was captured by German troops on 9 April 1940 at Horten, commissioned by the German Navy as KMS Albatross. On May, 3, 1945 she was heavy damaged at Kiel by American plans, sinking in the harbor. She also participated in the Battle of Horten Harbour. A complete separated article will detail every bit of this interesting ship in the future.

Specifications
Displacement: 1596 tons
Dimensions: 97.3 x 11.45 x 3.5 m
Propulsion: 2 De Laval Turbines, 2 Sulzer diesels, electric motors, 4600/1400 shp
Top speed: 14/21 knots (37.04 km/h)
Radius of Action: 3,000 nm (5,556.00 km) at 14 knots (25.93 km/h)
Armament: 4× 120mm (4.72 inch) Bofors, one 76 mm (3 inch) AA, 2 × 12.7 mm AA, 2x2? 46 cm TTs, 280 mines
Crew: 175
 Stern view of the mines ports, launching doors of KMS Brummer ex-Tryggvason (Bundesarchiv).
Stern view of the mines ports, launching doors of KMS Brummer ex-Tryggvason (Bundesarchiv).
GLOMMEN class minelayers (1917)
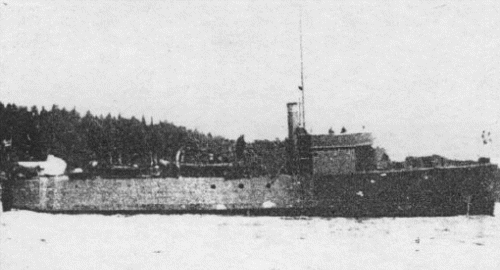
These coastal minelayers were built during the great war at Akers yards, Oslo, laid down in 1916, completed in 1917-18. They had been designed, tailored for service into the Oslo-Fjord. In April 1940 they operated in the area around Melsomvik. Glommen and Laugen were surrendered, captured by German troops on 14 April 1940 at Tunsberg, and re-commissioned as such, according to one source. According to another, they were rebuilt as floating flak batteries (Nki-01, Nki-02).KMS Glommen was later sunk by British aircrafts on 20 October 1940 in Trondheim-fjord (another source says she was scuttled at Kirkenes by the retreating Germans in 1944) while KMS Laugen survived and was retro-ceded to Norway after the war.
Specifications
Displacement: 351 tons
Dimensions: 42 x 8.5 x 2.3 m
Propulsion: 2 Reciprocating steam engines, 340 shp
Top speed: 9.9 knots (11.4 mph; 18.3 km/h)
Armament: 2x 76 mm/28 Bofors (another source: 2 × 76 mm (3 in) QF guns), 120 mines
Crew: 35
FRØYA minelayer (1917)

One of the few modern minelayers of Norway when ww2 broke out: Laid down at MV Horten in 1914 she was launched in 1916 and completed the next year, entering service before the end of the war. This was a seaworthy minelayer, very well armed for her limited displacement and, she was fast. By many ways, she was a kind of blueprint for the development of he 1930s Olaf Tryggvason. In the mid-1930s she was modernized as her boilers were converted to mixed coal/oil firing and she carried 95 tons of coal and about 60 tons of oil and she had a 76 mm/28 Bofors. When the German invasion started, HNoMS Frøya was scuttled by her crew on April, 13, 1940 in the Skern-fjord (Trondheim).
In detail: She was underway from Finnmark to Horten naval base (Oslofjord) on 8 April, stopping at Brekstad harbour, Ørland, just at the mouth of the Trondheimsfjord. Captain T. Schrøder-Nielsen at first declined to cross Hustadvika bay due to the very bad weather and fog, znd tried instead to seek shelter at Brekstad. In the morning of April, 9, the crew spotted German warships approaching, on their way to Trondheim. Trapped, the captain decided to sail into the nearby Stjørnfjord. However the minelayer was soon spotted and repeatedly attacked by recently landed artillery and Luftwaffe bombers.
On 13 April, Schrøder-Nielsen decided to scuttle the ship, having lost hope. Sensitive Equipment was removed, and Frøya's mines load as well for possible later use. The ship was rammed at great speed ashore at Søtvika. The hull's valves were opened, explosive detotaned. The ships was later spotted by Kapitänleutnant Wilhelm Rollmann (U-34) and she torpedoed the Frøya, believing she was still recoverable.
Specifications
Displacement: 595 tons
Dimensions: 75.3 x 8.2 x 2.8 m
Propulsion: 2 shafts TE engines, 6,000 hp
Top speed: 22 knots (40.74 km/h)
Armament: 4x 102mm/37 Bofors, 2x 450 mm TT, 180 mines
Crew: 78
Gor class gunboats (1885)
Gor and Tyr were about the same type as the following ships: In 1914, both were converted to minelayers with a single 263 mm/27 gun plus one 120 mm/44 Armstrong Y and carried 55 mines. In the 1920s both ships were rearmed again, Gor with a 37 mm/20 and a 76 mm/28 Bofors and Tyr with a single 57 mm/40 and single 47 mm/46 Bofors. Gor was captured by the German minesweeper М1 off Bremanger in May, 13, 1940, and re-commissioned as an auxiliary. Tyr was captured on 20 April 1940 by the a German armed trawler at Uskedal, and re-commissioned under own name, and later returned to Norway and scrapped.
Brage class gunboats (1879)
Brage and Nor were built at MV Horten, and about the same type as Vale. They were armed with British guns, and like the Vale class, in 1913, both were converted to minelayers, keeping their 267 mm/14 gun and 37 mm/20 piece, plus 149 mm/45 Armstrong FF gun, 47 mm/46 Hotchkiss gun and carried 50 mines, while their displacement rose to 255/270t. Both were captured by the Germans at Tonsberg on 14/4/1940 and served as auxiliaries until the end of the war. A very close vessel was built in 1882 Vidar. She was converted as a minelayer in 1913, rearmed like the two others, captured like them on 14/4/1940 at Tonsberg, and re-commissioned by Germans as NK31. She was scrapped in 1945.

VALE class gunboats (1874-77)
Built at MV Horten they were amongst the oldest vessels in service worldwide when ww2 broke out. These were of the British-design "Elswick" type, with one heavy gun. In 1913, both were converted to minelayers, but they kept their 267 mm/14 RML gun, and single aft 120 mm/44 Armstrong gun, but carried 50 mines. Displacement rose to 238t up to 250t.
Brief specs: 250 tons, 27.3 x 7.9 m, 2 VC engines, 2 boilers, 200 hp, 8 knots, 22 tons of coal, crew 38. Uller was captured by German troops off Bergen, recommissioned but on May, 2,1940 sunk by a Norwegian aircraft in Sogne-fjord. Vale was captured by German minesweeper М1 off Bremanger in May 1940, and recommissioned as an auxiliary vessel. Fate unknown. She was liely broken up or scuttled in 1945.